Glossary
| m-type | morphological type |
| e-type | electrical type |
| me-type | morpho-electrical type |
| s-type | synapse type |
| Intrinsic | efferent fibres arising from within the neocortical microcircuit |
| Extrinsic | efferent fibres arising from outside the neocortical microcircuit |
| Synaptic contact | a direct apposition between the axon and dendrites or soma |
| Synaptic connection | the set of all synaptic contacts between the presynaptic axon and the postsynaptic dendrites or soma |
| Synaptic connection-type (pathway) | the set of all connections between pairs of neurons of pre and postsynaptic m-types |
| Branch order |
the number of bifurcations between an axonal or dendritic section and the soma. Branch order is denoted by °. For e.g., 1° refers to the first dendritic branch originating from the soma or the main apical dendrite |
| Path distance | the distance between a given section and the soma measured along the axon or dendrites |
| Innervation pattern | a histogram of the locations of synapses measured by branch order or path distance |
| Neuronal convergence | the total number of neurons of one m-type targeting a single neuron of another m-type |
| Neuronal divergence | the total number of neurons of one m-type targeted by a single neuron of another m-type |
| Resting membrane potential (Vm) | the membrane potential (in mV) of a single neuron when potential (Vm) electrically inert or in resting state |
| Membrane time constant (τm) | the time taken (in ms) for the neuronal membrane to charge or discharge |
| Input resistance (Rin) | is given by Ohm's law from the difference in membrane potential of a single neuron at the point of a current injection to after it has reached a steady state (Rin=∆V/∆I MΩ) |
| gsyn | the peak conductance (in nS) for a single synaptic contact |
| Use | utilization of synaptic efficacy - analogous to the transmitter release probability at a single synaptic contact |
| Dep | time constant (in ms) for recovery from depression |
| Fac | time constant (in ms) for recovery from facilitation |
| PSP | the postsynaptic membrane potential change (in mV) evoked by a presynaptic stimulus; typically an injection of a brief pulse or a train of pulses to the presynaptic soma |
| Latency | the onset time (in ms) measured as the difference between the time to peak of the presynaptic AP and time taken to reach 5% of peak PSP amplitude |
| Amplitude | the difference in the membrane potential (in mV) measured between the peak and baseline |
| Rise time | the mean time (in ms) to rise from 20% to 80% of peak PSP amplitude |
| Decay time constant | the mean time (in ms) to decay from peak PSP amplitude to baseline constant |
| Transmission failure | an event where the presynaptic stimulus fails to evoke a postsynaptic response |
| c.v. of PSP | the coefficient of variation of the PSP amplitude measured as the ratio of SD and mean |
List of single cell stimulus protocols
| IDRest | Step current injection in soma. Current amplitude is a percentage of the rheobase. |
| APThreshold | Ramp current inject in soma. Current amplitude is a percentage of the rheobase. |
| APWaveform | High resolution (higher sampling frequency) short step current injection in soma. Typically elicits 1 or 2 action potentials. |
List of m-types
| DAC | Descending Axon Cell |
| NGC-DA | Neurogliaform Cell with dense axonal arborization |
| NGC-SA | Neurogliaform Cell with slender axonal arborization |
| HAC | Horizontal Axon Cell |
| LAC | Large Axon Cell |
| SAC | Small Axon Cell |
| MC | Martinotti Cell |
| BTC | Bitufted Cell |
| DBC | Double Bouquet Cell |
| BP | Bipolar Cell |
| NGC | Neurogliaform Cell |
| LBC | Large Basket Cell |
| NBC | Nest Basket Cell |
| SBC | Small Basket Cell |
| ChC | Chandelier Cell |
| PC | Pyramidal Cell |
| SP | Star Pyramidal Cell |
| SS | Spiny Stellate Cell |
| TTPC1 | Thick-tufted Pyramidal Cell with a late bifurcating apical tuft |
| TTPC2 | Thick-tufted Pyramidal Cell with an early bifurcating apical tuft |
| UTPC | Untufted Pyramidal Cell |
| STPC | Slender-tufted Pyramidal Cell |
| TPC_L4 | Tufted Pyramidal Cell with apical dendrites terminating in layer 4 |
| TPC_L1 | Tufted Pyramidal Cell with apical dendrites terminating in layer 1 |
| IPC | Pyramidal Cell with inverted apical-like dendrites |
| BPC | Pyramidal Cell with bipolar apical-like dendrites |
List of s-types
| I1 | Inhibitory, facilitating |
| I2 | Inhibitory, depressing |
| I3 | Inhibitory, pseudo-linear |
| E1 | Excitatory, facilitating |
| E2 | Excitatory, depressing |
| E3 | Excitatory, pseudo-linear |
List of e-types
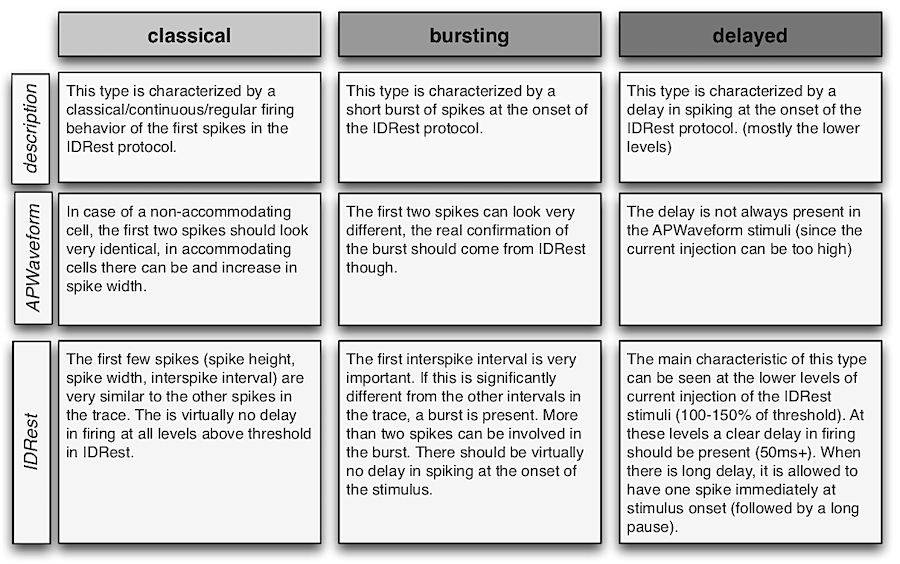
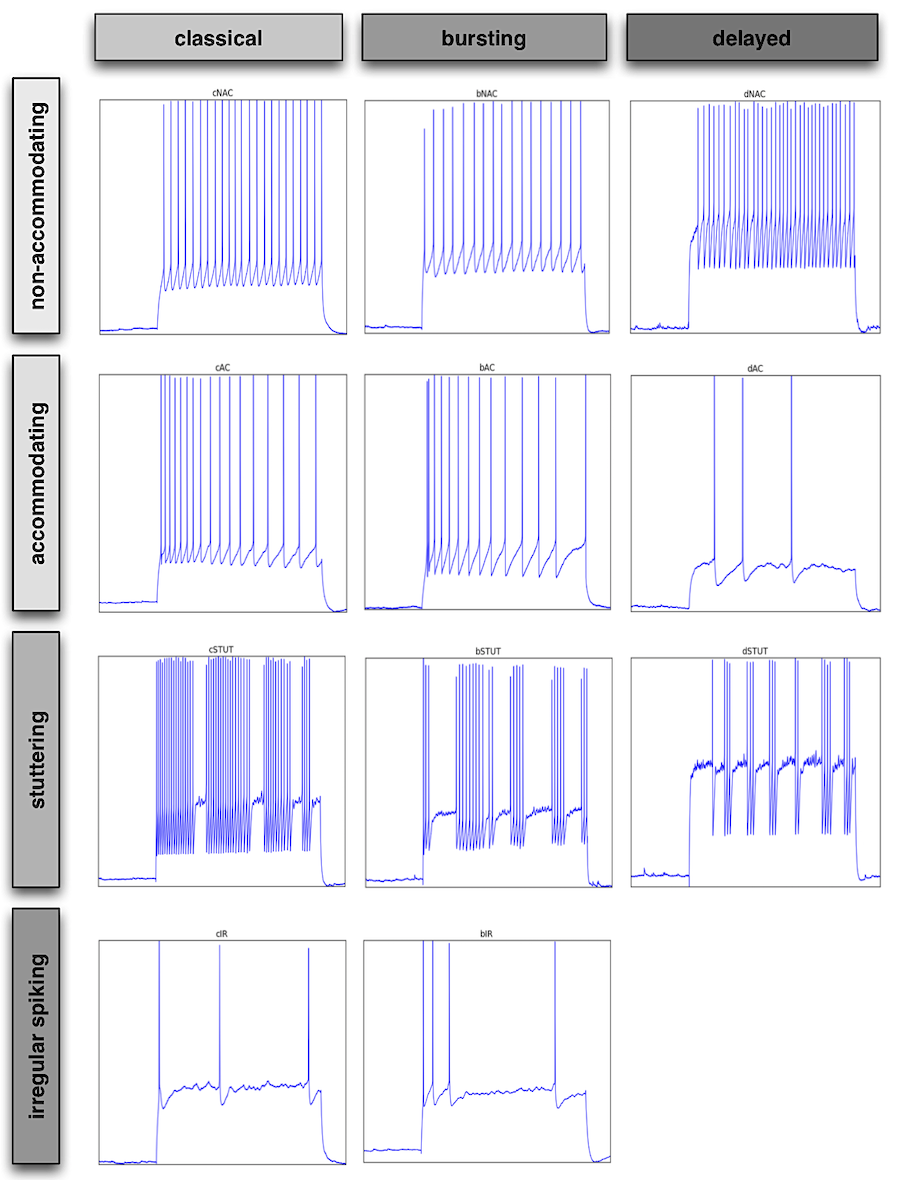
| cADpyr | continuous Accommodating (Adapting) for pyramidal cells |
| cAC | continuous Accommodating |
| bAC | burst Accommodating |
| cNAC | continuous Non-accommodating |
| bNAC | burst Non-accommodating |
| dNAC | delayed Non-accommodating |
| cSTUT | continuous Stuttering |
| bSTUT | burst Stuttering |
| dSTUT | delayed Stuttering |
| cIR | continuous Irregular |
| bIR | burst Irregular |
Spike Characteristics
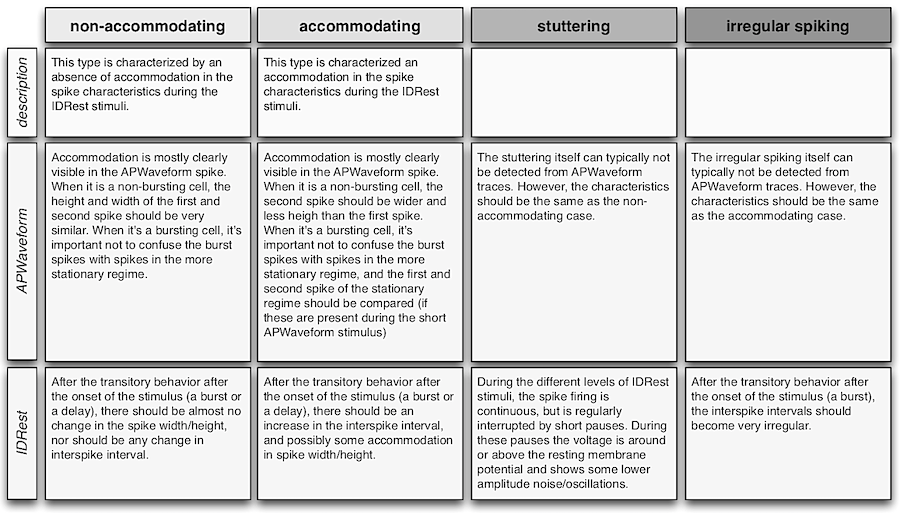
Firing Behavior